The Future of Manufacturing: Exploring the Innovations in 3D Metal Printing

3D metal printing is shaking up the manufacturing world in a big way. It's like something out of a sci-fi movie, but it's happening right now. This tech is not just a fancy tool; it's changing how we think about making things. From cars to planes, and even medical devices, 3D metal printing is opening doors we didn't even know existed. And the best part? It's just getting started. As we dive into this topic, we'll see how it's not only transforming industries but also paving the way for a future where the impossible becomes possible.
Key Takeaways
- 3D metal printing is revolutionizing manufacturing, offering new possibilities for design and production.
- This technology is being adopted across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and healthcare.
- Innovations in materials and technology are driving the growth and capabilities of 3D metal printing.
- Despite its advantages, challenges like cost and technical limitations remain to be addressed.
- The future of 3D metal printing looks promising, with potential for widespread adoption and impact.
Revolutionizing Production with 3D Metal Printing

Understanding the Basics of 3D Metal Printing
3D metal printing, also known as metal additive manufacturing, is all about building metal parts layer by layer. This process starts with a digital model, which is sliced into thin layers. Then, a printer lays down metal powder or filament, melting it with a laser or electron beam to form each layer. This repeats until the part is complete. This method allows for intricate designs that traditional manufacturing struggles with.
Key Advantages Over Traditional Manufacturing
When compared to traditional methods, 3D metal printing offers several perks:
- Cost Efficiency: It cuts down on waste since only the needed material is used.
- Customization: Easily create unique parts without needing new molds or tools.
- Speed: Faster prototyping and production cycles mean quicker time-to-market.
Industries Leading the Adoption
Several industries are at the forefront of adopting 3D printing technology:
- Aerospace: Companies like Boeing are using it for lightweight, strong components, reducing both weight and cost.
- Automotive: Enables rapid prototyping and production of durable parts.
- Healthcare: Custom implants and prosthetics are tailored to individual needs.
The shift towards 3D metal printing is not just a trend; it's a transformation. Industries are finding that the ability to quickly adapt and innovate is key to staying competitive. As more sectors embrace this technology, the possibilities seem endless.
Innovative Materials in 3D Metal Printing

Exploring New Metal Alloys
3D metal printing is changing the game by bringing in new metal alloys that were once tough to work with. These advanced alloys are making it possible to create parts that are stronger, lighter, and more heat-resistant than ever before. Industries are now using alloys like titanium and aluminum to make super complex parts that are both durable and lightweight. This is especially important in sectors like aerospace and automotive, where every ounce counts.
The Role of Composite Materials
Composite materials are also stepping into the spotlight in 3D printing. By blending metals with ceramics or polymers, these composites offer a unique mix of strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear and tear. This blend is perfect for applications that demand high performance under stress. For instance, metal-ceramic alloy composites are gaining traction for their exceptional properties in high-stress environments.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Options
As 3D printing evolves, there's a big push towards using eco-friendly materials. Manufacturers are exploring ways to reduce waste and energy consumption. The focus is on materials that can be recycled or that have a smaller carbon footprint. This shift not only helps the environment but also cuts down on costs in the long run. Plus, innovative techniques like enhancing the absorptivity of metal powders with nanoscale features are leading to improved efficiency and quality in the printing process.
The future of 3D metal printing is not just about making things faster or cheaper; it's about making them better for the planet too. By focusing on sustainable practices, the industry is paving the way for a greener future.
Technological Advancements Driving 3D Metal Printing
The Impact of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are making waves in 3D metal printing. These technologies are helping to fine-tune the printing process by predicting and correcting errors before they happen. AI-driven software can analyze complex designs and optimize them for printing, ensuring a higher success rate. Machine Learning algorithms are also being used to monitor the printing process in real-time, adjusting parameters on-the-fly to maintain quality.
Enhancements in Printing Speed and Precision
Speed and precision are critical in 3D printing, and recent advancements are pushing these boundaries. New technologies, like Hexagon's advanced compensation technology, are making it possible to print metal components faster without sacrificing precision. This technology removes much of the guesswork, leading to more accurate prints. Additionally, improvements in laser technology and powder delivery systems are significantly reducing print times while maintaining high detail levels.
Integration with IoT and Smart Manufacturing
The Internet of Things (IoT) is playing a pivotal role in transforming 3D metal printing into a smart manufacturing process. By connecting printers to a network, manufacturers can monitor and control the printing process remotely. This integration allows for better resource management and reduces downtime. Smart sensors and data analytics provide insights into machine performance, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing unexpected breakdowns. As we move towards Industry 4.0, the synergy between IoT and 3D printing will likely grow, enhancing efficiency and productivity across the board.
Challenges and Solutions in 3D Metal Printing
Overcoming Technical Limitations
3D metal printing is a marvel of modern engineering, but it's not without its hitches. One of the major technical hurdles is the inconsistency in material properties. Unlike traditional manufacturing, where materials are uniform, 3D printing can result in parts with varying density and strength. This variability can cause parts to fail unexpectedly. Another issue is the limited range of metals that can be used effectively. While new alloys are being developed, the technology still lags behind traditional methods in terms of material diversity.
To tackle these problems, researchers are focusing on improving the precision of printing techniques and developing post-processing methods to enhance material consistency. Additionally, advancements in metal filament 3D printing are paving the way for more reliable and diverse material options.
Addressing Cost and Accessibility
The cost of 3D metal printing can be prohibitive for many businesses. High initial investment in equipment and materials, along with the need for skilled operators, can make it a less attractive option compared to traditional methods. Moreover, access to 3D metal printing technology is still limited to larger companies or specialized industries.
To make this technology more accessible, there is a push towards developing more affordable printers and materials. Companies are also exploring service models that allow smaller businesses to utilize 3D metal printing without the need for significant upfront investment. Additionally, training programs are being implemented to build a workforce capable of operating and maintaining these advanced machines.
Ensuring Quality and Consistency
Quality assurance in 3D metal printing is another significant challenge. Parts need to meet stringent standards, especially in industries like aerospace and medical, where failure is not an option. However, given the layer-by-layer construction of 3D printed parts, ensuring uniform quality is complex.
Innovative solutions are being developed to address these quality concerns. For instance, real-time monitoring systems are being integrated into printers to detect and correct errors as they occur. Moreover, technology developers are working on advanced inspection techniques to ensure that each part meets the required specifications before it leaves the production line.
"The road to perfecting 3D metal printing is paved with challenges, but each obstacle also presents an opportunity for innovation and improvement."
Future Trends in 3D Metal Printing

Predictions for the Next Decade
The next ten years in 3D metal printing are set to be transformative. Expectations include faster, cheaper, and more precise printing technologies. As materials science advances, we'll likely see new metal alloys that offer enhanced strength and durability. The integration of AI and machine learning will play a crucial role in optimizing printing processes, predicting failures, and improving design capabilities. Moreover, the 3D printing market is anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 23.5% through 2024, with North America spearheading this expansion.
Emerging Applications and Use Cases
Industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare are leading the charge in adopting 3D metal printing. In aerospace, for instance, the ability to produce lightweight, complex parts is a game changer. The defense sector is also seeing significant advancements, with notable progress in creating robust components. In healthcare, custom implants and prosthetics tailored to individual patients are becoming more feasible and affordable.
The Role of 3D Printing in Industry 4.0
3D metal printing is a key player in the Industry 4.0 revolution, where smart manufacturing and digitalization are the norms. By integrating with IoT, 3D printing allows for real-time monitoring and quality control, enhancing the production line's efficiency. The resilience of 3D printing companies is evident, with only 35% reporting decreased sales in fall 2024, showcasing the industry's stability and growth potential. As manufacturing becomes more automated, 3D printing will help bridge the gap between digital designs and physical products, driving innovation across various sectors.
Case Studies: Success Stories in 3D Metal Printing
Automotive Industry Innovations
In the automotive world, 3D metal printing is shifting gears. Car manufacturers are embracing this technology to create lighter, more efficient parts. For instance, some companies are using 3D printing to produce engine components that not only cut down on weight but also improve fuel efficiency. This approach allows for rapid prototyping, enabling quicker iterations and testing. As a result, the time from design to production is significantly reduced, offering a competitive edge.
Aerospace Breakthroughs
The aerospace sector is soaring with 3D metal printing innovations. Northrop Grumman has demonstrated this by slashing the production time for rocket motor tooling from a year to just six weeks. This leap in efficiency not only speeds up development but also cuts costs. The ability to produce complex parts with intricate geometries has opened new frontiers in aerospace design, enabling the creation of components that were previously impossible to manufacture.
Medical and Healthcare Applications
In healthcare, 3D metal printing is a game-changer. Custom implants and prosthetics tailored to individual patients are now a reality, thanks to this technology. Surgeons can work with precise models for pre-surgical planning, improving outcomes and reducing operation times. This personalized approach to medical devices enhances patient comfort and functionality, marking a significant advancement in medical care.
With the continued evolution of 3D metal printing, industries are not just keeping pace with technological advancements—they're setting new standards in innovation and efficiency. The potential applications seem limitless, from automotive breakthroughs to life-saving medical devices.
The Economic Impact of 3D Metal Printing
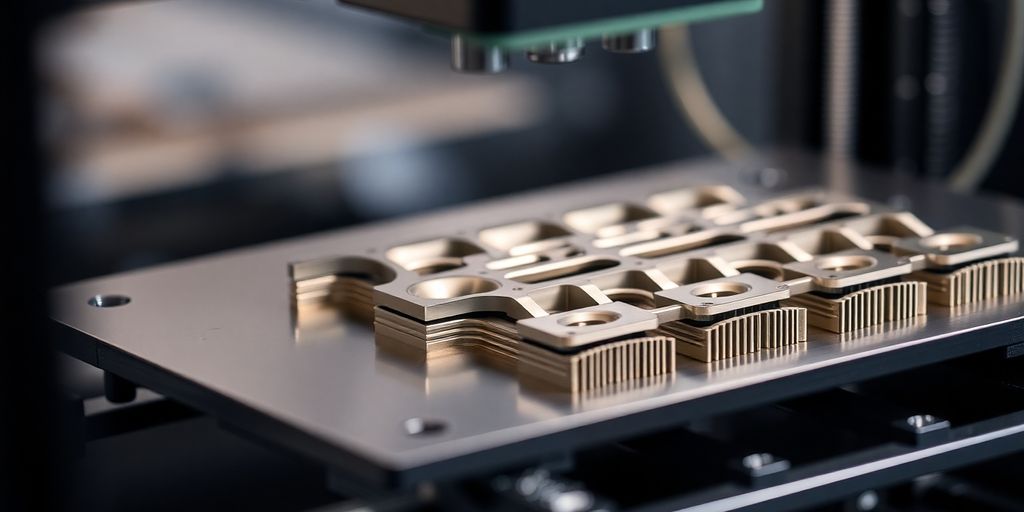
Job Creation and Workforce Transformation
3D metal printing is not just about machines and materials; it's reshaping the workforce landscape. As industries integrate this technology, new roles are emerging, from design engineers to machine operators specializing in additive manufacturing. While some traditional manufacturing jobs may be at risk, the demand for skilled workers in 3D printing is on the rise, offering opportunities for retraining and upskilling.
- New Job Roles: As 3D printing becomes more mainstream, roles such as 3D design specialists, machine maintenance experts, and quality assurance analysts are becoming crucial.
- Upskilling Opportunities: Current employees can be trained to handle new technologies, ensuring they remain relevant in the evolving job market.
- Education and Training: Institutions are beginning to offer specialized courses in additive manufacturing, preparing the next generation for these new careers.
Cost Efficiency and Return on Investment
The cost dynamics of manufacturing are changing with 3D metal printing. Traditional methods often involve significant material waste and long production times. In contrast, additive manufacturing builds items layer by layer, which can significantly reduce waste and shorten production cycles.
- Material Savings: By using only the material needed, 3D printing reduces waste, which can lead to cost savings.
- Faster Production Times: The ability to quickly prototype and produce parts means products can reach the market faster, potentially increasing revenue.
- Reduced Inventory Costs: With on-demand production, companies can minimize inventory, reducing storage costs and waste.
Global Market Growth and Opportunities
The global market for 3D metal printing is on a steep upward trajectory. With a projected market growth from $2,478.5 million in 2024 to $10,893.1 million by 2032, the industry is set for significant expansion. This growth is driven by advancements in technology and material science, making 3D metal printing more accessible and affordable.
- Expanding Applications: From aerospace to healthcare, more industries are finding innovative applications for 3D metal printing.
- Investment Opportunities: As the market grows, so do investment opportunities, attracting venture capital and fostering innovation.
- International Expansion: Companies are exploring global markets, leveraging 3D printing to meet diverse needs across different regions.
The shift towards 3D metal printing is not just a technological evolution but a transformative economic force, reshaping industries and creating new pathways for growth and innovation.
As we move forward, addressing socio-economic concerns such as job displacement while maximizing the technology's benefits will be crucial for sustainable growth.
Conclusion
3D metal printing is shaking up the manufacturing world, and it's just getting started. This tech is not just about making things; it's about changing how we think about making things. From aerospace to healthcare, industries are jumping on board, seeing the benefits of faster production times and the ability to create complex designs that were impossible before. Sure, there are challenges, like figuring out the best materials and processes, but the potential is huge. As we move forward, 3D metal printing could redefine manufacturing, making it more efficient and adaptable. It's an exciting time, and who knows what we'll be able to print next?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 3D metal printing?
3D metal printing is a way of making things by adding layers of metal one at a time. It's like regular 3D printing but uses metal instead of plastic.
How does 3D metal printing work?
It starts with spreading a thin layer of metal powder. A laser then melts the powder to form a solid layer. This process repeats until the whole object is made.
What are the benefits of 3D metal printing?
3D metal printing can make complex shapes that are hard to create with traditional methods. It also reduces waste and can be faster for making custom parts.
Which industries use 3D metal printing?
Industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare use 3D metal printing to create parts that are lightweight, strong, and custom-designed.
Is 3D metal printing expensive?
While the machines can be costly, 3D metal printing can save money by reducing material waste and speeding up production times.
What is the future of 3D metal printing?
3D metal printing is expected to grow, with more materials and faster printers. It will likely become a key part of manufacturing in many industries.




